Lydia Amazouz Published on December 28, 2024
Collected at: https://dailygalaxy.com/2024/12/5g-satellite-transform-global-connectivity/
In a groundbreaking development that could redefine global communication, 5G technology has, for the first time, successfully connected directly to a low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite. The achievement, spearheaded by the European Space Agency (ESA) in collaboration with Telesat, marks a monumental leap toward making satellite-based internet as accessible as terrestrial networks. This breakthrough not only has the potential to extend high-speed connectivity to remote areas but also sets the stage for revolutionary advancements in sectors like healthcare, disaster response, and autonomous technology.
The Science Behind the Breakthrough
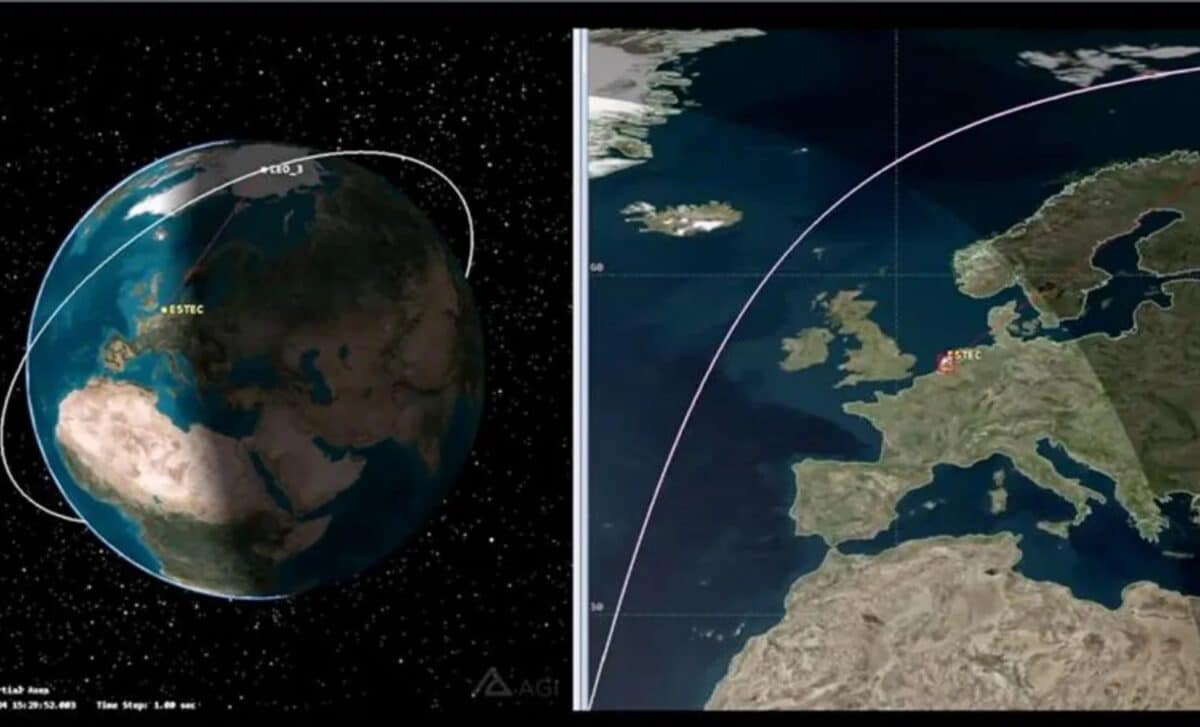
The ESA’s collaboration with Telesat began with a Memorandum of Understanding, granting access to Telesat’s LEO 3 satellite for testing. Unlike geostationary satellites that remain fixed relative to the Earth, LEO satellites travel rapidly, requiring advanced technology to maintain a stable connection. This experiment relied on Amarisoft’s 5G Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) technology, which enabled a continuous connection as the satellite moved from the horizon to its peak elevation of 38 degrees and back down again.
This achievement validates the feasibility of seamless communication between ground-based networks and LEO satellites. “This world-first experiment demonstrates ESA’s technical excellence in advancing broadband satellite access technology,” stated Alberto Ginesi, ESA’s Head of the Telecom Systems and Techniques Section of the Directorate of Technology, Engineering, and Quality (TEC).
The success builds on 3GPP standardization group specifications, which ensure compatibility between mobile networks and satellite systems. This adherence to open standards is critical for the eventual implementation of “direct-to-device” satellite connections, where smartphones and devices connect seamlessly to satellites without additional infrastructure.
Why This Matters: Connectivity Without Limits
The implications of this breakthrough are far-reaching. By bridging the gap between terrestrial and satellite networks, it paves the way for a range of innovative applications. For example:
- Disaster Response: Rapid and reliable communication is essential during natural disasters, particularly in areas where traditional infrastructure has been destroyed. Satellite-based 5G could provide a lifeline in such scenarios.
- Telehealth: Remote surgery and healthcare services could become more accessible, even in isolated locations, thanks to ultra-low-latency communication.
- Autonomous Vehicles: With uninterrupted connectivity, self-driving cars and drones could operate more efficiently in rural or urban areas with patchy ground-based networks.
- Global Internet Access: Communities in underserved and remote regions could gain access to high-speed internet, bridging the digital divide.
“Building on the 3GPP standardisation groups’ approval, we’ve proven 5G NTN specifications over a real non-geostationary orbit satellite link. Through this achievement, we’ve shown ESA’s capability to support advanced satellite broadband networks, paving the way for upcoming projects such as IRIS²,” Ginesi explained, adding that the contributions of Augusto Marziani, Stefano Cioni, and Matteo Conti were instrumental in the success of the experiment.
Open Standards: A Key to Future Integration
One of the most significant aspects of this experiment was the use of open standards instead of proprietary technology. The Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP), an international body that develops telecommunication standards, played a crucial role in ensuring interoperability between different systems. Open standards are vital for scaling this technology globally, reducing costs, and enabling seamless switching between ground-based networks and satellite connections.
This approach represents a departure from older proprietary systems that often required specialized hardware and software. With open standards, the vision of connecting everyday mobile devices directly to satellites becomes more achievable. The possibilities include lowering infrastructure costs, enhancing interconnectivity between providers, and simplifying access to high-speed internet.
A Glimpse Into the Future: IRIS² and Beyond
The ESA’s achievement lays the groundwork for ambitious future projects, including IRIS², the European Union’s flagship satellite communications initiative. By building on the success of this experiment, IRIS² aims to provide secure and resilient satellite-based communications for a variety of applications, from national security to commercial services.
The potential for satellite 5G technology extends far beyond Europe. Countries and organizations around the world are closely watching this development, as it offers a scalable solution for bridging connectivity gaps in remote regions and improving global interconnectivity. As 5G NTN technology matures, its integration with LEO satellites could revolutionize how people access the internet, transforming it into a truly global network.
Challenges Ahead: From Testing to Real-World Applications
While this breakthrough is a significant milestone, challenges remain before it can be implemented on a large scale. Establishing widespread infrastructure, ensuring compatibility across devices, and maintaining cost-effectiveness will require coordinated efforts between governments, private companies, and international organizations. Additionally, regulatory hurdles may slow the rollout of satellite-based 5G in certain regions.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits are immense. The ESA’s successful test proves that the technology is not only feasible but also highly promising. As development continues, the dream of global connectivity, accessible to anyone regardless of location, moves closer to reality.
Revolutionizing Connectivity Through Space
The ESA and Telesat’s pioneering 5G connection to a LEO satellite marks a historic moment in communication technology. By proving the viability of satellite-based 5G, this experiment opens the door to a future where high-speed internet is available everywhere—from urban centers to the most remote corners of the globe. As projects like IRIS² build on this foundation, the way we think about connectivity is poised for a radical transformation.
For now, this world-first achievement serves as a reminder of how innovation and collaboration can push the boundaries of what is possible, reshaping industries and improving lives worldwide. The sky, quite literally, is no longer the limit.

Leave a Reply