December 23, 2024 by University of Tsukuba
Collected at: https://phys.org/news/2024-12-printable-laser-emitting-droplets-display.html
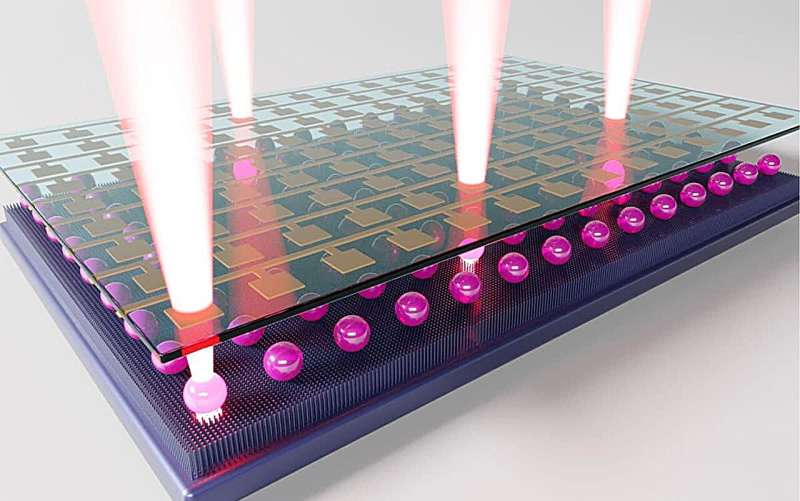
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba have developed an innovative method for rapidly creating laser light sources in large quantities using an inkjet printer that ejects laser-emitting droplets.
By applying an electric field to these droplets, the researchers demonstrated that switching the emission of light on and off is possible. Furthermore, they successfully created a compact laser display by arranging these droplets on a circuit board.
The study is published in Advanced Materials.
Displays for TVs, PCs, and smartphones are continually improving in picture quality, clarity, and energy efficiency. Laser displays are anticipated to represent the next-generation model. Particularly regarding brightness and color reproducibility, laser displays have the potential to overcome the intrinsic limitations of conventional light-emitting devices, such as OLEDs and liquid crystals.
However, to be effectively used as displays, the components must be miniaturized beyond current levels and laid out in high density and large quantities.
In this study, the researchers found that droplets of a specific organic liquid, ejected by an inkjet printer, emit laser light. The laser light can be switched on and off by applying an electric field to the droplets. These droplets are extremely small (30 µm in diameter) and can be densely arranged in large quantities over areas as large as several centimeters.
When an electric field is applied to the droplet by positioning it between electrodes, the spherical droplet deforms into an ellipsoidal shape, causing the laser light emission to cease.
This demonstrated that the droplet functions as an electrically switchable “laser pixel.” Additionally, the researchers discovered that the laser emission of each pixel can be individually controlled in a 2×3 array of these droplets.
Further improvements in the configuration of electrical devices and laser performance are expected to contribute significantly to the future development of commercial laser displays.
More information: Masato Kato et al, Optically Pumped and Electrically Switchable Microlaser Array Based on Elliptic Deformation and Q‐Attenuation of Organic Droplet Oscillators, Advanced Materials (2024). DOI: 10.1002/adma.202413793
Journal information: Advanced Materials

Leave a Reply