
By: Qualcomm and RCR Wireless News (Sponsored) November 6, 2024
Sensors have become seamlessly embedded into a wide array of devices, from smartphones and wearables to vehicles and more, making them integral to how we understand and interact with our surroundings. They enhance our daily experiences by supporting a diverse range of applications, enabling more informed decisions and efficient interactions with the environment around us.
The true value of sensors lies in their ability to ultimately generate actionable insights from the raw data they collect, highlighting the importance of constant connectivity. This is why wireless technologies, such as cellular, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and ultra-wide band (UWB) have become the backbone of sensor connectivity.
Interestingly, did you know that the same radio frequency (RF) signals used for wireless communication can also function as sensors? This blog post uncovers the concept of wireless sensing and the potential of its integration with communications in the 6G era, a powerful combination known in the industry as Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC). Read on to discover how ISAC can bring many benefits and exciting new possibilities.
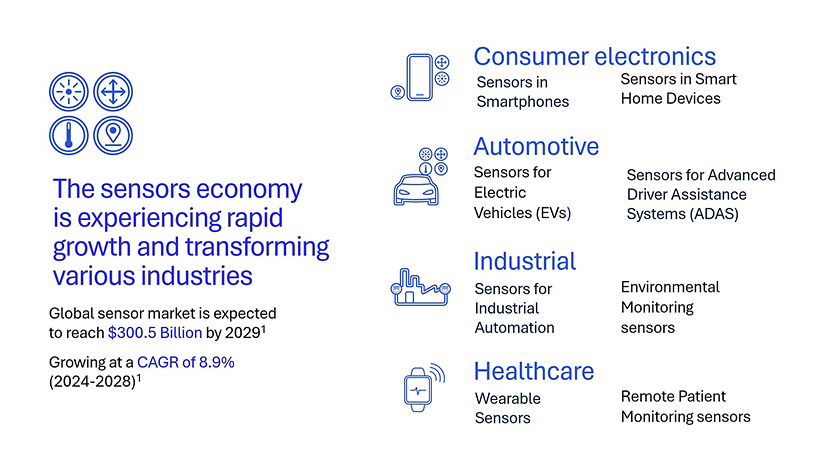
Figure 1. Strength of the sensor economy continues to grow and transform industries.
What is wireless sensing?
Wireless sensing is an innovative technology that utilizes RF signals to detect the environment — all without the need for active electronics on the sensing target. It can enable spatial monitoring without using cameras, and is capable of presence detection, motion and gesture recognition, and even environmental monitoring.
Wireless sensing works by detecting and analyzing changes in RF signals as they travel from a transmitter to a receiver. It can flexibly support different operation modes, tailoring to specific needs. Monostatic sensing integrates the transmitter and receiver within a single entity, allowing for self-contained, compact implementation. On the other hand, bistatic sensing supports the transmitter and receiver in different entities, offering more flexibility. Additionally, multistatic sensing utilizes multiple receivers to detect signals from one or more transmitters, further improving performance.
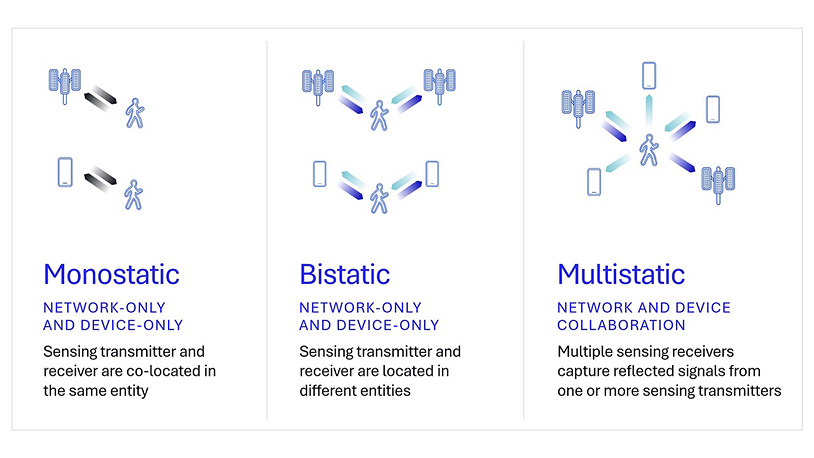
Figure 2. Wireless sensing offers flexible operation modes for different use case scenarios.
What use cases can benefit from wireless sensing?
This emerging wireless capability is set to enable a wide range of use cases. For instance, wireless sensing can enhance drone operations by enabling collision avoidance, flight trajectory tracing and intrusion detection. Other use cases include intruder detection in smart homes, geo-fencing in smart factories, and unobtrusive vital monitoring in healthcare. There are many other examples shown in Figure 3 highlighting the diverse use of wireless sensing in enhancing safety, efficiency and convenience. Many of these are actively being studied in the wireless ecosystem and broader industries.

Figure 3. Wireless sensing can support a variety of use cases across industries.
What is 6G ISAC and why is it important for the ecosystem?
The convergence of wireless sensing and communication presents an exciting opportunity, particularly as we approach the advent of 6G around 2030. This next-generation network will be designed with a native system architecture that supports a wide array of services beyond communications. From day one, 6G is expected to leverage the transformative potential of AI and advanced computing, while also incorporating wireless positioning and sensing capabilities.
By integrating wireless sensing and communication into a single system design, ISAC can significantly improve system efficiency, maximizing hardware reuse for both communications and sensing such as RF components and computation resources. Improved spectral efficiency is another benefit. ISAC can reduce wireless interference and eliminate the need for separate spectrum allocations for sensing and communications. Moreover, a unified system design can enhance energy efficiency by sharing power and processing resources, resulting in more streamlined operations.
The integration of sensing technology into wireless networks marks a significant leap forward in both economic and operational domains. Initially, it can bring new revenue streams by enabling innovative vertical use cases, such as enhanced drone operations and advanced healthcare monitoring. Furthermore, the integration of sensing capabilities with digital twin networks can substantially boost network efficiency. Digital twins, which are models of the physical systems in the digital realm, represent a key 6G application set to transform network management and operations. By leveraging real-time wireless sensing to continuously improve digital twins, network operators can significantly improve efficiency, performance and cost savings.

Figure 4. 6G ISAC delivers tangible network efficiency benefits.
Where are we now on the path to 6G ISAC?
The journey to 6G ISAC begins with the 5G Advanced Study Item focusing on wireless sensing services. Comprehensive studies on channel modeling, various sensing modes, robust system requirements, multiple use cases and specific key performance indicators (KPIs) are laying the groundwork for these next-generation capabilities.
At Qualcomm Technologies, we are advancing wireless sensing through cutting-edge research and prototyping. During Mobile World Congress 2024, we showcased our latest high-resolution sensing system utilizing higher-frequency bands, and capable of monostatic and bistatic operation modes and multiple objects identification. This advancement enables sophisticated applications like identifying material types based on their RF characteristics, which is very useful for the accurate creation and maintenance of digital twin models.
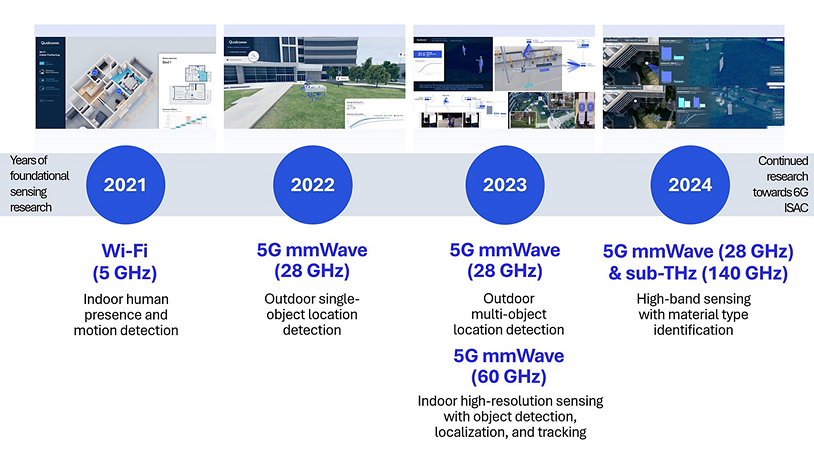
Figure 5. Advancing wireless sensing through cutting-edge research and prototyping.
What’s next?
The vast potential of wireless sensing, being developed as 6G ISAC, holds the promise of transformative impact across numerous industries. Realizing these breakthroughs will require substantial effort, and we are excited to be driving this progress forward. As we unlock the possibilities of 6G, we remain excited about its future and invite you to follow our journey as these innovations unfold.

Leave a Reply